
Wireless exploitation is the practice of footprinting (sniffing), analyzing and manipulating wireless data. This section describes some tips, resources and references to help solve wireless exploitation challenges.
Key Concepts (WiFi):
- SSID – service set identifier is the name for a Wi-Fi network
- MAC Address – Media Access Control address is the factory assigned physical address.
- Access Point – device that acts as a communication hub for wireless users connecting to the network
- IP Address – Internet Protocol (IP) address is an identifier for a device on a TCP/IP network.
- Wireless Encryption:
- Wireless Standards – Determines the modulation, speed and security available (e.g., 802-11, 802-11a, 802-11g, etc.)
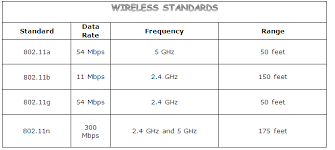
Security Standards:
- Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) – Old security algorithm for IEEE 802.11 wireless confidentiality using a 10 or 26 hex digits. Vulnerable to attacks on packet integrity.
- Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) – Uses a 64 or 128-bit encryption key (TKIP) that dynamically generates a new keys for each packet and a Message Integrity Check (MIC) to address WEP weaknesess.
- WPA-2 Includes mandatory support for CCMP, an AES-based encryption mode.
- WPA-3 – uses a 192-bit cryptographic strength in WPA3-Enterprise mode (AES-256 in GCM mode with SHA-384 as HMAC), uses of CCMP-128 (AES-128 in CCM mode).

Recommended Steps for Vulnerability Assessments:
- Footprint – Scan the wireless landscape and identify network resources for exploitation.
- Wigle.net – If you have the SSID of the access point to get physical location information.
- Packet Capture – Use tools like Wireshark to capture and analyze packets (includes SSID , MAC addresses (OmniPeek maps MAC addresses) and Encryption Mode).
- Analysis – Based on footprint data, search for known vulnerabilities (e.g., plain text passwords, weak encryption, CVEs, etc.) to determine the exploit.
- Crack Wifi Access Passwords – Use Aircrack-ng (recommended) or hashcat to crack the access point WEP and WPA PWs (link)
- Investigate Potential Exploits:
- Evil Twins / Man-in-the-Middle – Fake WiFi Access Points
- Packet Sniffing – Interception of Unencrypted Traffic
- Wardriving – Identify and map vulnerable access points.
- Warshipping – Remote attack to WiFi network
- MAC Spoofing – spoof a MAC address and bypass this wifi controls.
Recommended Tools:
- ToolBench:
- Kali Linux – Linux suite of cybersecurity tools
- Wireshark – packet analysis for network card in promiscous mode.
- Aircrack- ng – recommended tool to assess WiFi security and crack WEP, WPA and WPA2 passwords
- hashcat – password cracking utility for WPA (if aircack-ng does not work)
- Ifconfig – ‘ ifconfig wlan0 down’ shutdown interface
- Footprinting:
- Wigle.net – Wifi info database for hotspots from around the world
- NetStumbler (set SSID to ANY) active mode (Windows)
- Kismet : both war-drive and sniffer. Uses passive mode (Linux)
- GPSMap : comes with Kismet and plots AP locations in maps, using ImageMagick,
- Packet Capture:
References:
- Crack WPA/WPA2 Wi-Fi Routers with Aircrack-ng and Hashcat
- Youtube: Why is Free WiFi Dangerous? Simply Explained. (8:21)
- Youtube: Wireless Network Technologies – CompTIA Network+ N10-007 – 1.6 (10:46)
- Youtube: Wireless Standards – CompTIA Network+ N10-007 – 1.6 (06.22)
- Youtube: Wireless Encryption – CompTIA Network+ N10-007 – 4.3 (04:01)
- Youtube: Wireless Authentication and Security – CompTIA Network+ N10-007 – 4.3 (05:13)
- Youtube: Rogue Access Points – CompTIA Network+ N10-007 – 4.4 (00:00)
- Youtube: Wireless Deauthentication – CompTIA Network+ N10-007 – 4.4 (05: 08)
- Youtube: NMap 101: Scanning Networks For Open Ports To Access, HakTip 94 (11:14)
- Youtube: HakTip – WiFi 101: 802.11 Protocols (10:xx)
- Youtube: HakTip – WiFi 101: Frame Analyzing (10:03)
- Wireless Network Tools
- What is SSID
- Explore & Map Nearby Wireless Networks with WiGLE [Tutorial] (13:14)