
Computer Network is an interconnection of multiple devices using multiple paths for the purpose of sending/receiving data or media. Multiple devices/mediums (e.g., routers, switches, hubs, and bridges and protocol rules are used to support the communication.
Key Concepts:
- Network – Computers or devices connected in some way to exchange data.
- Types of area networks – Local (LAN), Metropolitan (MAN) and Wide (WAN) area networks.
- Network Topology: Physical Layer connections (e.g., Bus, Star, Mesh, Ring, and Daisy chain)
- Network Protocols: set of rules or algorithms for communicating across the network
- OSI Framework – Protocol reference model that specifies 7 layers of standards for communications
- TCP/IP – Internet protocol suite standards used in computer networks (e.g., TCP, IP, UDP, ARP, DHCP, FTP, etc.).
- Network Data Units: Packaging formats for data transmission at different layers (e.g., bits, frames, packets, segments, data)
- Network Addresses:
- Domain Name – Assigned text label that identifies specific a Internet Protocol resource (i.e., yahoo.com).
- Sub Domain – part of a larger domain used to improve efficiency or control (i.e., blog.yahoo.com).
- IP Address: Numeric address string assigned to devices across the network ; Consists of 4 bytes separated by periods (e.g., 136.102.233.49):
- IPv4 address is 32-bits
- IPv6 address is 128-bits.
- MAC Address : physical address assigned by the manufacturer and is associated with its NIC (Network Interface Card). Type “ipconfig/all” .
- Network Port: logical channel used to send/receive data on a device (range of 0-65535 addresses with 216 ports available). (Type “netstat -a” )
- Network Socket: The unique combination of IP address and Port number that serves as an endpoint for sending and receiving data.
- Host name: associated with a unique device name known as Hostname. (type ‘hostname’)
- Address Servers:
- DNS Server: Domain Name system translates web addresses (URLs) into their corresponding IP addresses. (use ‘nslookup’)
- DCHP Server: Dynamically assigned an IP address when a device connects to the network
- Other Network Concepts:
- Software defined Networking (SDN)
- Virtual LAN (VLAN) – any broadcast domain that is partitioned and isolated in a computer network at the data link layer (OSI layer 2).
- Wireless (Wi-Fi) – wireless network protocols, based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves.
- Internet – global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate.
OSI Model:
The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model) standardizes the interoperability of diverse systems by using standard interface protocols (rules). The model partitions a communication connections into the following (7) OSI Layers.
- Layer 1: Physical (bits) – communicate unstructured raw data (bits) between physical devices.
- Layer 2: Data Link (frames) – sends frames within the existing wide area network or on the same local area network.
- Layer 3: Network (packets ) – transfers data (packets) from one node to another connected in a “different network”.
- Layer 4: Transport (segments) – transferring data (segments) to a destination host and ensure the data is received (quality).
- Layer 5: Session (data link) – control the dialogues (connections) between computers.
- Layer 6: Presentation (data link) – establishes context between application-layer entities (e.g., encryption, syntax, etc.)
- Layer 7: Application (data link) – interacts with software applications

TCP IP Model:
Network Addresseses
- MAC Address – Media Access Control Address is unique physical address of computer. Factory assigned in the NIC card for Layer2 Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). Six (6) bytes (48 bits) long.
- IP address – logical identifier of a network connection for a device. Network assigned for Layer3. Four (4) bytes (32 bits)
- Network Address Translation (NAT) – Private IP address or local address are translated into the public IP address.
- Port Address Translation (PAT) – Private IP addresses are translated into the public IP address via Port numbers.
Network Ports
A port number is used to connect to a Internet Protocol (IP) server and can be anything from 0 to 65535. The two common types of ports are TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol). Below are a few common ports to know by heart:
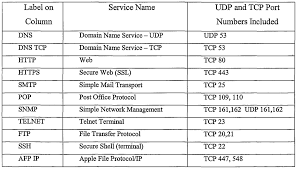
- 20 – FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
- 22 – Secure Shell (SSH)
- 25 – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
- 53 – Domain Name System (DNS)
- 80 – Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- 110 – Post Office Protocol (POP3)
- 143 – Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
- 443 – HTTP Secure (HTTPS)
TCP and UDP
- TCP and UDP Protocols:TCP Connection – 3 Way Handshake
- Common TCP and UDP Ports – Default ports
- IP Header Format – Incuded in PCAP file
- ICMP Protocol – used by network devices, including routers, to send error messages and operational information
Network Traffic Analysis files
- Network Packets – formatted unit of data carried by a packet-switched network. A packet consists of control information and user data;[1] the latter is also known as the payload.
- Pcap – Packet Capture File which includes: (1) Source and Destination port #s , (2) IP addresses , (3) Physical (MAC) addresses, (4) Protocol and Encryption info, (5) Header and Payload info, (6) Wireless info and other data. Use Wireshark or equivalent tool to analyze the PCAP.
Network commands
- ping – Linux (and Windows) command to measure the round-trip time for messages sent to a destination computer that are echoed back to the source. (e.g. ping google.com)
- Nmap – Discover hosts and services on a computer network by sending packets and analyzing the responses.
- traceroute – Linux command to measuring transit delays of packets across an Internet Protocol (IP) network
- netstat – a command-line utility that displays TCP connections (both incoming and outgoing), routing tables, network interface, and network protocol statistics (e.g., netstat -r, netstat -a, netstat -ie, etc.)
- ifconfig – command utility for displaying the network interface configuration. (e.g., ifconfig -a)
- host – When used with a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) the host command will return information associated with that name such as its IP address (e.g. host www.yahoo.com)
References
- Youtube: What is Networking? – Networking Basics (23:32)
- HakTip:
- Youtube: Linux Terminal 201: Networking Commands You Should Know! – HakTip 152 (09.51)
- Youtube: NMap 101: Scanning Networks For Open Ports To Access, HakTip 94 (8:50)
- Network+ Modules:
- Youtube: Network Types – N10-008 CompTIA Network+ : 1.2 (14:29)h
- Youtube: Network Communication – N10-008 CompTIA Network+ : 1.4 (5:27)
- Youtube: What is OSI Model? (08:22)
- Youtube: Data Communication – N10-008 CompTIA Network+ : 1.1 (12:46)
- Youtube: Common Ports – CompTIA Network+ N10-007 – 1.1 (13:11)
- Youtube: IPv4 Addressing – N10-008 CompTIA Network+ : 1.4 (9:16)
- Youtube: IPv6 Addressing – N10-008 CompTIA Network+ : 1.4 (13:17)
- Youtube: IPv4 Subnet Masks – N10-008 CompTIA Network+ : 1.4 (8:40)
- Youtube: Seven-Second Subnetting – N10-008 CompTIA Network+ : 1.4 (20:11)
- Youtube: Configuring VLANs – CompTIA Network+ N10-006 – 2.6 (07:10)
- Youtube: NCL Summer LIVE – HTTP & HTTPS – July 22 2021 (50:04)
- Youtube; TCP Fundamentals Part 1 // TCP/IP Explained with Wireshark (xx:xx)
- Youtube: How TCP Works – The Handshake
- Networking Fundamentals – Module 1 (Practical Networking)
- Lesson 1 – Network Devices
- Lesson 2 – OSI Model
- Lesson 3 – Everything Hosts to do speak on the Internet
- Lesson 4 – Everything Switches do to facilitate communication
- Lesson 5 – Everything Routers do to facilitate communication
- Lesson 6 – Networking Protocols
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E5bSu… – ARP, FTP, SMTP, HTTP, SSL, TLS, HTTPS, DNS, DHCP – Four items MUST be configured for Internet Connectivity
- Lesson 7 – How Data moves through a Network
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YJGGY…
- – Network Engineering Interview question: What happens when you type “site.com” into a web browser?